Challenges: concurrency, competing user/signal interactions, responsiveness.
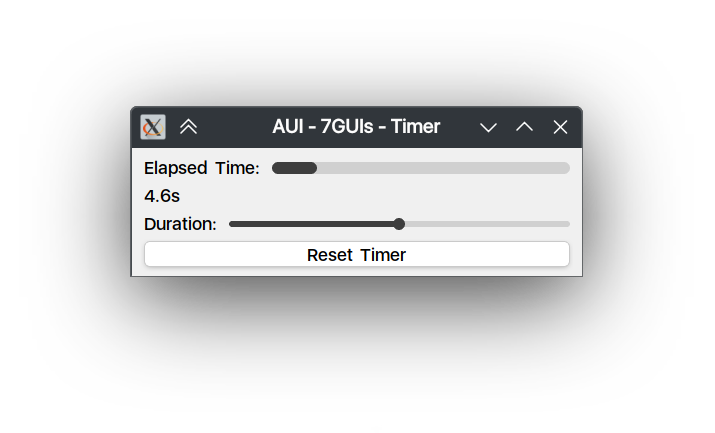
The task is to build a frame containing a gauge G for the elapsed time e, a label which shows the elapsed time as a numerical value, a slider S by which the duration d of the timer can be adjusted while the timer is running and a reset button R. Adjusting S must immediately reflect on d and not only when S is released. It follows that while moving S the filled amount of G will (usually) change immediately. When e ≥ d is true then the timer stops (and G will be full). If, thereafter, d is increased such that d > e will be true then the timer restarts to tick until e ≥ d is true again. Clicking R will reset e to zero.
Timer deals with concurrency in the sense that a timer process that updates the elapsed time runs concurrently to the user’s interactions with the GUI application. This also means that the solution to competing user and signal interactions is tested. The fact that slider adjustments must be reflected immediately moreover tests the responsiveness of the solution. A good solution will make it clear that the signal is a timer tick and, as always, has not much scaffolding.
#include <AUI/Platform/Entry.h>
#include <AUI/Platform/AWindow.h>
#include <AUI/Util/UIBuildingHelpers.h>
#include "AUI/View/AProgressBar.h"
#include "AUI/View/ASlider.h"
#include "AUI/View/AButton.h"
using namespace declarative;
using namespace std::chrono;
using namespace std::chrono_literals;
static constexpr high_resolution_clock::duration MAX_DURATION = 60s;
class TimerWindow :
public AWindow {
public:
TimerWindow() :
AWindow(
"AUI - 7GUIs - Timer", 300_dp, 50_dp) {
Vertical::Expanding {
Horizontal {
Label {
"Elapsed Time:" },
Centered::Expanding {
_new<AProgressBar>()
let {
it & mElapsedTimeRatio;
},
},
},
Label {} & mElapsedTime.readProjected([](high_resolution_clock::duration d) {
return "{:.1f}s"_format(duration_cast<milliseconds>(d).count() / 1000.f);
}),
Horizontal {
Label { "Duration:" },
it&& mDuration.biProjected(aui::lambda_overloaded {
[](high_resolution_clock::duration d) -> aui::float_within_0_1 {
return float(d.count()) / float(MAX_DURATION.count());
},
[](aui::float_within_0_1 d) -> high_resolution_clock::duration {
return high_resolution_clock::duration(long(float(d) * float(MAX_DURATION.count())));
},
});
it->setCustomStyle({ Expanding {} });
},
},
Expanding { 1, 0 },
},
});
connect(mTimer->fired, me::update);
mTimer->start();
}
private:
_<ATimer> mTimer = _new<ATimer>(100ms);
high_resolution_clock::time_point mStartTime = high_resolution_clock::now();
AProperty<high_resolution_clock::time_point> mCurrentTime;
AProperty<high_resolution_clock::duration> mDuration = 30s;
APropertyPrecomputed<high_resolution_clock::duration> mElapsedTime = [&] {
return std::min(mCurrentTime - mStartTime, *mDuration);
};
APropertyPrecomputed<aui::float_within_0_1> mElapsedTimeRatio = [&] {
return float(mElapsedTime->count()) / float(mDuration->count());
};
void update() { mCurrentTime = high_resolution_clock::now(); }
void reset() { mStartTime = high_resolution_clock::now(); }
};
_new<TimerWindow>()->show();
return 0;
}
void setContents(const _< AViewContainer > &container)
Moves (like via std::move) all children and layout of the specified container to this container.
Represents a window in the underlying windowing system.
Definition AWindow.h:45
static decltype(auto) connect(const Signal &signal, Object *object, Function &&function)
Connects signal to the slot of the specified object.
Definition AObject.h:82
#define let
Performs multiple operations on a single object without repeating its name (in place) This function c...
Definition kAUI.h:262
#define with_style
Allows to define a style to the view right in place.
Definition kAUI.h:287
#define AUI_ENTRY
Application entry point.
Definition Entry.h:90
Controls the expanding of AView.
Definition Expanding.h:26
Declarative form of ALabel.
Definition ALabel.h:35